Jillian Cooper
How Relocated Beavers Fight Climate Change
Relocated beavers cooled stream temperatures and restored the water levels only a year after their arrival.
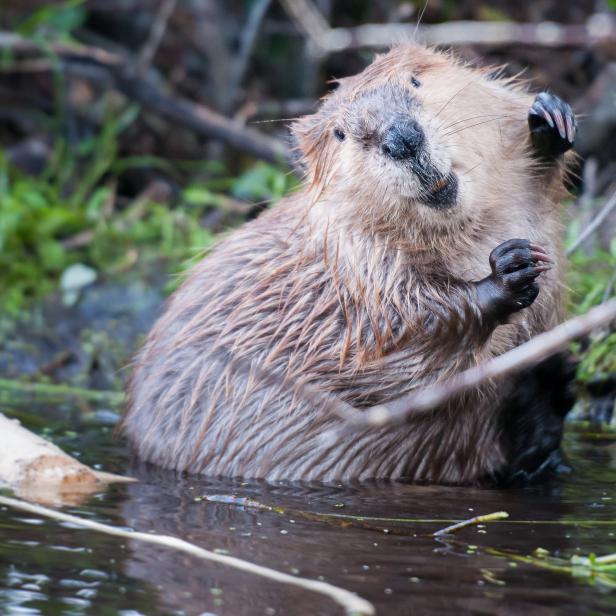
Busy beavers have turned out to be an effective tool in alleviating certain effects of climate change within water ecosystems.
A colony of seven beavers was moved to a new home along the Skykomish River from a lake near Seattle and set to work on building a new dam, increasing water storage and lowering stream temperature by about 2 degrees Celsius.
The region around the Skykomish River has been affected by the effects of climate change. Less snow has caused the river to grow warmer which can be fatal for the salmon population who live there.
Beavers instinctually build dams, ponds, and wetlands, for their homes. The dams then slow down the flow, restoring cooler water temperatures and raising water tables.
At five of the sites where beavers were relocated, they built 14 dams. The construction of those dams increased the volume of surface water in the area by about 20 times that of streams with no new beaver activity.
Researchers hope to study beavers' impact on further restoration efforts into the next generation as they mate and raise their kits that form new colonies.